Soil CBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 9
→ Soil is a naturally occurring substance that is valuable in sustaining life on earth.
→ Many microorganisms live in the soil.

- Humus: It is a component of soil that is formed from the dead and decayed organic matter.
- Weathering: It is the process of formation of soil by breaking down of rocks. It occurs by the action of wind, water, and climate.
Soil Profile
→ It is a vertical section through various layers of soil.
→ These various layers are known as horizons.

There are four types of horizons:
- A-horizon or topsoil: It is the top most soil, which is dark in colour and rich in humus. It is soft, porous, and has the ability to retain water.
- B-horizon: It is the middle next layer of the soil profile. It has lesser humus and more minerals. The layer is harder and more compact.
- C-horizon: It is the third layer made up of small lumps of rocks with cracks and crevices.
- Bedrock: It is the lowermost hard layer and difficult to dig with a spade.
How is Soil Formed?
In the first stage of soil formation, the soil is generally non-porous in nature. Then it slowly turns into soil having air and water in the pores.
We can define soil as a mixture of rock particles and humus. Based on the size of the particles and the textures of the soil, it can be divided into various types.

Soil Types
→ Soil is a mixture of rock particles and humus.
→ Living organisms such as microbes, earthworm, and plant roots are found in soil.

Classification of soil
- Sandy soil
- Sand particles are large that cannot fit together.
- Larger spaces are present between particles.
- It is light, well aerated, and dry.
- Clayey soil
- Clay particles are smaller and tightly packed together.
- It has little space for air and can hold water between particles.
- Loamy soil
- It is the best top soil for the growth of plants.
- It is the mixture of sand, clay, and silt.
- It contains humus and has the right water holding capacity.
- Toys, pots, and statues are made up of clayey soil.
- Silt soil
- The soil particles are smaller than that of sandy soils but larger than clayey soils.
- Silt Soil can hold water to some extent because of its fine quality.
- They are generally found near the water bodies like river banks and lakes.

Properties of Soil
→ Percolation rate of water varies in different soil types.
Percolation rate (mL/min) = amount of water (mL) / percolation time (min)

→ Percolation rate of water is highest in sandy soil and least in clayey soil.
→ The soil moisture and water absorption capacity of soil also varies among different soil types.
→ Loamy soil has the maximum accurate water holding capacity while sandy soil has the least.
→ Climatic factors such as wind, rainfall, temperature, light, and humidity affect the soil.
Soil and Crops
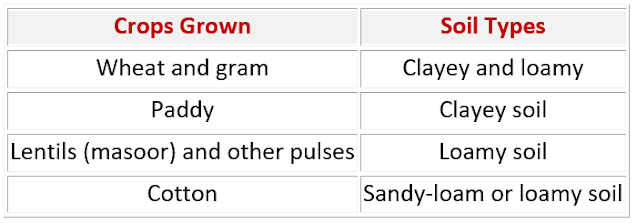
→ The soil capacity to hold water is important for the cultivation of various crops.
Crop
→ When same kinds of plants are cultivated on a large scale, it is called a crop.
It is of two types:
- Kharif crops
- Crops that are sown in rainy season (June to September)
- Examples – soyabean, paddy, maize
- Rabi crops
- Crops that are grown during winter season (October to March)
- Examples – wheat, gram, pea
Basic Crop Production Practices
- Preparation of soil
- Sowing
- Adding manure and fertilizers
- Irrigation
- Protection from weeds (weeding)
- Harvesting
- Storage
Factors Leading to Soil Pollution
Various human activities and products pollute the soil. These pollutants destroy the fertility of the soil and harm the organisms living in the soil.
- Polythene bags
- Plastic products
- Chemicals
- Pesticides
→ The preventive measures that can be adopted to reduce soil pollution are as follows:
- Treating the waste products before disposal
- Reducing the use of polythene bags
- Minimizing the use of products made of plastic
- Minimizing the use of pesticides
- Plastic particles and polythene bags are banned to avoid soil pollution.
Soil Erosion
→ When the top layer of soil gets removed it is called soil erosion.
→ The soil erosion mainly occurs when the soil is left loose without vegetation or when deforestation occurs.
→ In such a condition, the action of wind, water, and human activities can wash away the topsoil.
Conservation of Soil
→ Prevention of soil erosion is important for conserving the soil.
→ Methods of soil conservation include:
- Terracing
- Contour farming
- Afforestation
- Gully plugging
- Building dams and check dams





0 Comments