The Verbs - @pratapsanjaysir
Verb
➥ A verb is a word that shows an action or state of being.
➥ Every sentence needs a verb to be complete.
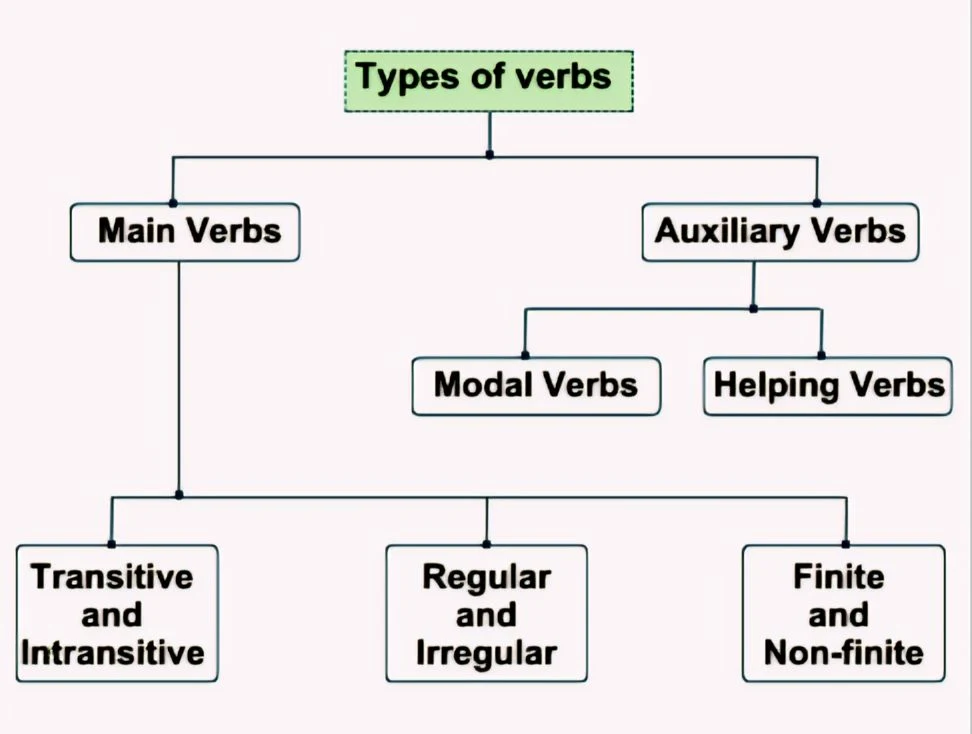
Types of Verbs
1. Main (Principal) Verbs
➥Main verbs are two types: - (i) transitive & (ii) intransitive.
- Transitive Verbs: These verbs require an object to complete their meaning.
- Examples: She kicked the ball.
He bought a book.
Explanation:- In the above examples, the verbs kicked and bought need objects (ball, book) to complete their meaning.
- Examples: She kicked the ball.
- Intransitive Verbs: These verbs do not need an object to complete their meaning.
- Examples: The baby cried.
He sleeps peacefully.
Explanation:- These verbs do not need objects to make sense.
- Examples: The baby cried.
2. Auxiliary (Helping) Verbs
➥ Helping verbs assist the main verb to form tenses, moods, or voices.
➥ There are two types:
(i) Primary Auxiliary Verbs
➥ These are the most common helping verbs and are used with the main verbs to show tense or form questions and negatives.
Examples:
- Be: is, am, are, was, were
- Have: has, have, had
- Do: do, does, did
Sentence Examples:
- She is reading a book.
- They have finished their homework.
- He does not like chocolate.
(ii) Modal Auxiliary Verbs
➥ Modal auxiliaries express necessity, possibility, permission, or ability.
Examples: can, could, may, might, will, would, shall, should, must
Sentence Examples:
- She can swim.
- You must study for the exam.
- He might come tomorrow.
Forms of Verbs
| Verb Form | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Base Form | The original form of the verb, used in the present tense. | go, write, eat |
| Past Tense | The form used to talk about something that happened in the past. | went, wrote, ate |
| Past Participle | Used with helping verbs like has or had to show completed actions. | gone, written, eaten |
| Present Participle | Used to show ongoing action, usually ending with -ing. | going, writing, eating |
Tenses of Verbs
➥ Verbs can be used in different tenses:
- Present Tense: Describes actions happening now.
- Examples: I play football.
He runs fast.
- Examples: I play football.
- Past Tense: Describes actions that happened before.
- Examples: I played football yesterday.
She danced beautifully.
- Examples: I played football yesterday.
- Future Tense: Describes actions that will happen in the future.
- Examples: I will play football tomorrow.
They will go to the park.
- Examples: I will play football tomorrow.
Regular and Irregular Verbs
- Regular Verbs: These verbs form their past tense by adding -ed to the base form.
- Examples: play → played, jump → jumped
- Irregular Verbs: These verbs do not follow the -ed rule for the past tense.
- Examples: go → went, eat → ate
Finite and Non-finite Verbs
(i) Finite Verbs
➥ A finite verb is a verb that agrees with the subject in terms of tense, person, and number.
- Examples: She works every day.
They played football yesterday.
(ii) Non-finite Verbs
➥ Non-finite verbs do not change their form according to the subject or tense. They include infinitives, gerunds, and participles.
- Examples:
- Infinitive: to write, to sing
- Gerund: writing, singing
- Participle: written, sung




0 Comments