📘 Excel 2016 – Formula and Functions Class 7 CBSE Notes
📘 Chapter 3: Formulas and Functions in Excel – By Pratap Sanjay Sir
Basic MS Excel
➥ MS Excel is a spreadsheet software developed by Microsoft. It helps in organizing, analyzing, and calculating data using tables made of rows and columns.
🔷 Basic Terms in Excel
- Workbook – A file that contains one or more worksheets.
- Worksheet – A single spreadsheet page consisting of rows and columns.
- Cell – The intersection of a row and a column (e.g., A1, B2).
- Cell Address – The name of a cell like
A1(Column A, Row 1). - Range – A group of selected cells (e.g.,
A1:C3).
🔷 Excel Window Components
- Title Bar – Shows the file name.
- Ribbon – Contains tabs like Home, Insert, Formulas, etc.
- Formula Bar – Displays the formula or value in the selected cell.
- Column Headings – A, B, C, ...
- Row Headings – 1, 2, 3, ...
- Active Cell – The current selected cell, shown with a border.
📘 Chapter 3: Formulas and Functions in Excel
🔷 1. Formula in Excel
A formula is an equation used to perform calculations.
It always begins with an equal sign =.
It can include numbers, cell references, operators, and functions.
📌 Example: =A1 + B1 → Adds values in cell A1 and B1.
🔷 2. Using a Range of Cells in a Formula
A range is a group of selected cells (e.g., A1:A5).
You can use ranges in formulas for operations like sum, average, etc.
📌 Example: =SUM(A1:A5) → Adds all values from cell A1 to A5.
🔷 3. Text Formula
Text formulas deal with combining text strings using the & (ampersand) symbol.
📌 Example: =A1 & " " & B1 → Combines text from A1 and B1 with a space in between.
🔷 4. Entering a Compound Formula
A compound formula includes multiple operators.
It follows the BODMAS rule (Brackets, Orders, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction).
📌 Example: =A1 + B1 * C1
🔷 5. Cell References
Cell references are the addresses of cells used in formulas.
🔷 6. Types of Cell References
- ✅ a) Relative Reference: Changes when the formula is copied.
Example:=A1+B1 - ✅ b) Absolute Reference: Remains constant when copied. Use
$sign.
Example:=$A$1+$B$1 - ✅ c) Mixed Reference: Only row or column is fixed.
Example:=$A1orA$1
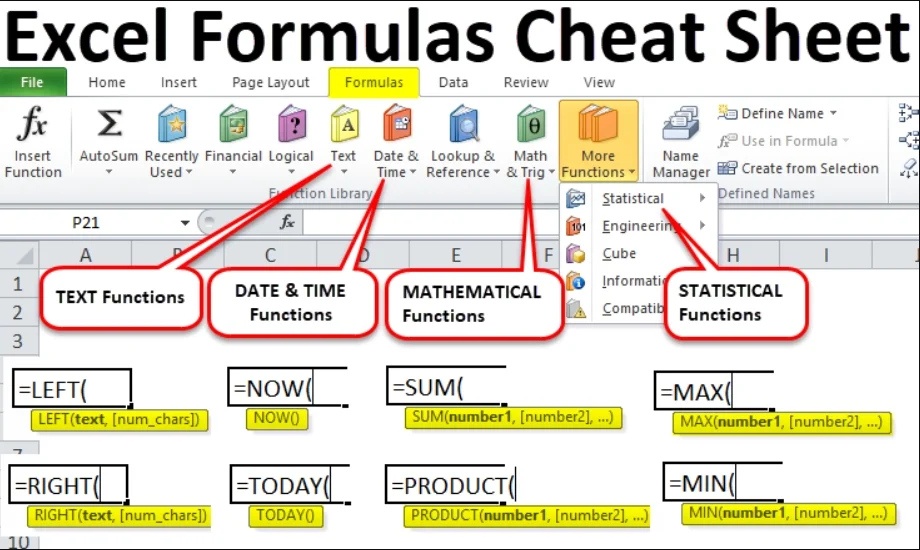
🔷 7. Functions in Excel
A function is a predefined formula to perform calculations quickly.
It always begins with = followed by the function name and arguments in brackets.
🔷 8. Types of Functions
✅ a) Mathematical Functions
| Function | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
SUM() | =SUM(A1:A5) | Adds all numbers |
PRODUCT() | =PRODUCT(A1:A5) | Multiplies all values |
POWER() | =POWER(2,3) | 2 raised to 3 = 8 |
✅ b) Statistical Functions
| Function | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
AVERAGE() | =AVERAGE(A1:A5) | Returns average |
MAX() | =MAX(A1:A5) | Returns highest value |
MIN() | =MIN(A1:A5) | Returns lowest value |
✅ c) Text Functions
| Function | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
UPPER() | =UPPER("excel") | Converts to uppercase |
LOWER() | =LOWER("EXCEL") | Converts to lowercase |
CONCAT() | =CONCAT(A1,B1) | Joins text |
✅ d) Date and Time Functions
| Function | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
NOW() | =NOW() | Displays current date and time |
TODAY() | =TODAY() | Displays today’s date |
✅ e) Logical Functions
| Function | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
IF() | =IF(A1>50, "Pass", "Fail") | Checks condition and returns value |
🔷 9. Entering a Function
Steps:
- Click the cell where you want to enter the function.
- Type
=FUNCTION_NAME(arguments)or use the Insert Function (fx) button.
🔷 10. Errors in Excel
Sometimes Excel shows errors if the formula is incorrect. Below are common errors:
| Error | Meaning |
|---|---|
#DIV/0! | Division by zero |
#VALUE! | Wrong type of argument |
#REF! | Invalid cell reference |
#NAME? | Typing mistake in function name |
Questions of Chapter 3: Formulas and Functions in Excel
A. Tick (✔) the Correct Answer
a. relative referencing
b. absolute referencing
c. mixed referencing ✔
a. & ✔
b. SUM
c. MIN
a. CONCATENATE
b. LEN ✔
c. LOWER
a. SUM
b. MOD
c. MIN ✔
a. true
b. false
c. Both (a) and (b) ✔
B. Fill in the blanks
- Formulas are used to perform mathematical calculations on data in Excel.
- The number in the SQRT function must always be greater than 0.
- Logical functions are used to compare two or more values of data in cells.
- The #VALUE! error occurs when wrong arguments are used within a formula.
- An error margin is defined as the extent of possible difference between calculated and true value.
C. True or False
- You are only allowed to add individual cell addresses in a formula.❌ – False
- The & is a text operator.✅ – True
- Using a cell address in a formula is called cell reference.✅ – True
- Making a cell reference fixed is referred to as relative referencing.❌ – False
- A function name is case sensitive. ❌– False
D. Answer the following questions
1. What is a compound formula? How can you add one in Excel?
A compound formula uses more than one operator (+, –, *, /). Example: =A1+B1*C1
2. What is the basic difference between relative and absolute referencing?
- Relative reference changes when copied (e.g., A1).
- Absolute reference is fixed using $ symbol (e.g., $A$1).
3. Write down the types of functions in Excel.
- Mathematical
- Text
- Statistical
- Logical
- Date and Time
4. Give examples to explain the use of MOD and SQRT functions.
- =MOD(10, 3) returns 1 (remainder).
- =SQRT(25) returns 5 (square root).
5. How can you fix the #REF! error?
Check and correct the cell reference in the formula that may have been deleted or moved.
E. Definitions
1. Text operator: Used to join text strings. Example: "Hello" & "World"
2. Mixed referencing: A cell reference that is partly absolute and partly relative, e.g., $A1 or A$1
3. Argument: The values passed inside a function. Example: =SUM(A1:A5) – A1:A5 is the argument.
4. Mathematical functions: Functions used for calculations. Example: SUM(), MOD(), SQRT()




0 Comments